In practical teaching, the improvement of teaching quality and experimental conditions of Electrical Control and Programmable Controller has not improved students’enthusiasm for learning. It is necessary to reform the experimental teaching mode.
The experimental teaching reform of Electrical Control and Programmable Controller is conducive to the improvement of learning. Students’enthusiasm and learning efficiency, enhance classroom interaction. Electrical Control and Programmable Controller is a highly operational and practical course for electrical engineering specialty. To learn this course well, it is necessary to exercise the ability of software programming. Experimental teaching plays a very important role. In 2015, our institute implemented the small-class teaching reform of the course, with 30-35 students in each class, purchased more than 10 sets of new Qianlong PLC training devices and equipped with SIMATIC S7-300 PLC and the latest configuration software of SIMATIC_STEP_7_V13, touch screen, frequency converter and other equipment to ensure that every 2-3 people have a set of experimental devices. But in the teaching of 2015, the improvement of experimental teaching quality is not directly proportional to the improvement of experimental hardware conditions, and students’initiative and enthusiasm are still not high. The traditional experimental teaching mode needs to be reformed urgently. Seminar teaching is a kind of teaching method originating from German universities in the 18th century. It has become an important teaching method in foreign universities by creating problem situations by teachers, searching for information by students, researching, discussing, practicing and exploring, and putting forward solutions to problems, which embodies the principle of student subjectivity. Small class teaching provides a strong guarantee for the smooth implementation of seminar learning. Based on the “six-step” discussion teaching method, the author designed the experimental teaching method of “Electrical Control and Programmable Controller” which centered on group cooperation. Practice shows that the designed teaching method has remarkable effect on improving students’enthusiasm, innovative ability and team spirit, as well as enhancing the relationship between teachers and students. In the early experimental teaching, the group members are freely combined. The advantage of this combination is that the group members are familiar with each other, but it leads to serious differentiation between groups.
Some groups are excellent students, and some groups are poor students. In the latter stage of teaching, the author optimizes the composition of the group, dividing the students into three levels according to their performance points: good, medium and poor. Each group is evenly matched by good, medium and poor students, so as to achieve good student supervision, promotion and promotion of poor students, and give full play to the advantages of group cooperation. The design of group cooperative seminar-centered experimental teaching method as shown in the right figure, the specific operation is as follows: 1. Task assignment (classroom orientation): This step is a week in advance by the teacher in the classroom to briefly describe the purpose of the experiment and control tasks, give possible solutions, and designate appropriate after-school reference materials (including the reference books of the campus library). Relevant chapters, e-sharing resources on the network, etc.
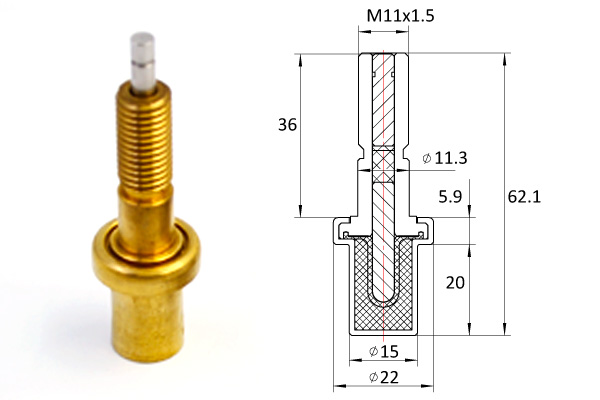

2. Reading materials: After class, students consult the relevant literature according to the experimental requirements, independently design the experimental circuit wiring diagram, assign the PLC I/O interface, and draw the control flow chart. Teams are encouraged to innovate boldly, not confined to the schemes designated by teachers. 3. System design: This step requires each group to discuss and complete after class. Each group member introduces his own experimental design scheme to the other members of the group. The group members fully communicate and cooperate with each other, discuss and determine the final design scheme, and write the corresponding program code as far as possible. 4. Program discussion: This step is the core of group cooperation and discussion teaching, thermostatic element which is conducted by the teacher in the experimental class (the time is controlled in 15-20 minutes). Teachers select 2 to 3 groups, and select students of different levels of good, medium and poor in each group.

In class, they report the experimental design plan of each group through blackboard or PPT. According to the design plan of each group, the teacher raises questions about its key steps and related important knowledge points, guides the whole class to discuss, and helps each group to improve the optimal design plan through teacher-student interaction. Teachers should give timely suggestions on Revision of the design plan for the group that is not feasible, and encourage and supervise the group to improve the design plan. In the process of discussion, teachers should not only be good directors, but also good actors and critics.
By carefully designing questions and comments, they can improve the attention of all students, fully mobilize the enthusiasm of all students, avoid teachers’questions, a few students answer and others do nothing. At the same time, teachers should pay close attention to and guide 2-3 students with poor grades, give them more opportunities to show and show, enhance their confidence and enthusiasm for learning. In addition, in order to better enhance students’awareness of participation, we can set up a score rule to encourage speech and challenge. 5. Experiments validation: Each group compiles programs according to the design scheme, debugs online, observes the output, and reaches the experimental requirements.
In these processes, teachers should instruct and answer questions on the spot according to the design plan of each group. 6. Achievement assignment: In this step, the teacher examines each group’s experimental operation one by one, evaluates each group’s score through quantitative scoring rules, and in order to prevent lazy students from “fishing in muddy water”, the teacher should put forward 1 or 2 questions to each student in the group according to the experimental procedure written by each group, and make a distinctive judgement through the answer of the questions. The results of each student. In order to objectively and comprehensively evaluate the experimental results of students, the author introduces the assessment method combining process evaluation with result evaluation. The total score of students’experiment is 100, which consists of group score (70%), students’ speech score (10%), students’self-assessment score (10%) and experimental report score (10%). The group score includes group design score (30%) and experimental result score (70%). The introduction of process evaluation avoids the traditional assessment method based on experimental results, which is conducive to improving students’enthusiasm for active participation in group discussions and fostering the spirit of self-learning and teamwork. By comparing the experimental teaching effect in 2015 and 2016, the group cooperation and discussion-centered teaching method has achieved better results. The students who “wait, depend and play” in the experimental class have been significantly reduced, and the students’self-learning and team cooperation spirit has been greatly improved. At present, the author’s understanding is still superficial. How to further improve the cooperation of team members and how to design a more scientific assessment mechanism will be the focus of further exploration in future teaching.
